Tags
Window Sliding Technique
Published Oct 06, 2021
[
Introduction
This technique shows how a nested for loop in some problems can be converted to a single for loop to reduce the time complexity.
Problem
Given an array of integers of size ‘n’.
Our aim is to calculate the maximum sum of ‘k’
consecutive elements in the array.
Input : arr[] = {100, 200, 300, 400}
k = 2
Output : 700
Input : arr[] = {1, 4, 2, 10, 23, 3, 1, 0, 20}
k = 4
Output : 39
We get maximum sum by adding subarray {4, 2, 10, 23}
of size 4.
Input : arr[] = {2, 3}
k = 3
Output : Invalid
There is no subarray of size 3 as size of whole
array is 2.
Window Sliding Technique
The technique can be best understood with the window pane in bus, consider a window of length n and the pane which is fixed in it of length k. Consider, initially the pane is at extreme left i.e., at 0 units from the left. Now, co-relate the window with array arr[] of size n and pane with current_sum of size k elements. Now, if we apply force on the window such that it moves a unit distance ahead. The pane will cover next k consecutive elements.
Consider an array arr[] = {5, 2, -1, 0, 3} and value of k = 3 and n = 5
Applying sliding window technique
- We compute the sum of first k elements out of n terms using a linear loop and store the sum in variable window_sum.
- Then we will graze linearly over the array till it reaches the end and simultaneously keep track of maximum sum.
- To get the current sum of block of k elements just subtract the first element from the previous block and add the last element of the current block .
The below representation will make it clear how the window slides over the array. This is the initial phase where we have calculated the initial window sum starting from index 0 . At this stage the window sum is 6. Now, we set the maximum_sum as current_window i.e 6.

Now, we slide our window by a unit index. Therefore, now it discards 5 from the window and adds 0 to the window. Hence, we will get our new window sum by subtracting 5 and then adding 0 to it. So, our window sum now becomes 1. Now, we will compare this window sum with the maximum_sum. As it is smaller we wont the change the maximum_sum.
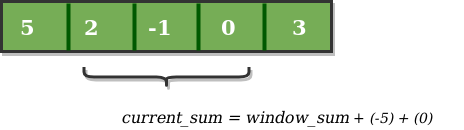
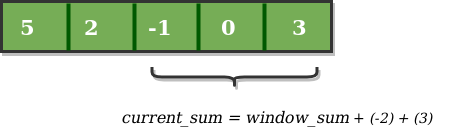
Similarly, now once again we slide our window by a unit index and obtain the new window sum to be 2. Again we check if this current window sum is greater than the maximum_sum till now. Once, again it is smaller so we don’t change the maximum_sum. Therefore, for the above array our maximum_sum is 6.
Code
// Javascript code for
// O(n) solution for finding
// maximum sum of a subarray
// of size k
function maxSumofK(arr, k) {
let max = 0;
let sum = 0;
//find initial sum of first k elements
for(let n = 0; n < k ; n++) {
sum += arr[n];
}
//iterate the array once and increment the right edge
for(let i = k; i < arr.length; i++) {
sum += arr[i] - arr[i-k];
//compare if sum is more than max, if yes then replace max with new sum value
if(sum > max) {
max = sum;
}
}
return max;
}
let arr = [1, 4, 2, 10, 2, 3, 1, 0, 20 ];
console.log(maxSumofK(arr, 4))
//output 28